September Privacy Roundup
Here's our September newsletter with major events from August - isn’t August meant to be quiet, or at least the silly season? Not in the world of Privacy...

We’ve had a bumper month of announcements and action. As always, we’ve curated the news that has the most practical impact on operationalising Privacy at your organisation.
We’ve practical updates in the fields of AI, US Privacy, transfers, breaches and practical jewels on using Facebook Pages, bulk emails and auto-complete, and ID verification.
First, a ground-breaking adequacy decision and it’s nothing to do with the UK or the EU!
California Adequacy from DFIC
The Dubai International Financial Centre’s Commissioner has issued, as it notes, a first-of-its-kind adequacy decision in favour of the state of California based on CCPA as amended by CPRA. Note this is not for the US, and not for a US-wide framework. This is the first adequacy decision for a single state in the USA.
As Ashkan Soltani, Executive Director of the California Privacy Protection Agency notes: ‘California is set to become the world’s 4th largest economy and is the de-facto leader in privacy in the U.S.’ The DFIC’s decision is brave, unique and to be applauded.
How important is this?
It’s hard to quantify the impact of this decision. The DIFC is an active, practical and very professional data protection authority with a law based on GDPR, so this is a powerful statement.
And California’s CCPA/CPRA has certainly pushed many states to pass or plan to pass comprehensive data protection law (the IAPP’s US state law tracker is a great resource). So the DIFC may well make other decisions favouring other states in due course.
But this decision isn’t available for entities outside the DIFC’s jurisdiction to use, such as UK or EEA entities. In the UK, we’re still waiting on the UK-US ‘data bridge’ piggy-backing the EU-US DPF already in place.
Outside immense interest to Privacy geeks, perhaps the most we can say for UK and EEA practitioners is that this decision is another strong, professional indication on the direction of Privacy in the US.
California Assessments (DPIAs)
OK, so it’s called risk assessment in California not DPIA, but we were talking about California …
The California Privacy Protection Agency has released draft Risk Assessment Regs. They contain proposed detail on when an assessment is required, with examples, and what an assessment must contain.
Happily, and as you’d expect, much is very familiar to EEA and UK DPIA guidance, and we’ll keep an eye on these regulations and assessments in the USA.

DPA’s Guidance on Bulk Email & Auto-Complete
Sensing emails to the wrong recipient is a consistent key cause of breaches reported to the UK ICO.
The UK ICO and the Danish DPA have now each issued guidance on the use of email to share personal data, particularly bulk email and auto-complete.
There’s lots of commonality between the guidance, with good practical information you can use in your policies and procedures. Here are 6 actions you can take now everyone’s back from summer.
- Consider whether to turn off auto-complete, if only for those users who regularly share personal data by email.
- Consider data sharing services and automated email services instead of your email solution.
- If you are using your email solution for bulk emails, consider the use of mail merge instead of BCC.
- Add a sending delay to emails (we love this ourselves).
- Always check recipient emails.
- Train your staff to beware of these accidental breaches, particularly those most likely to be sending personal data because of their role.
Factors to consider include which employees send personal data regularly, how sensitive that data is, how voluminous it is, and the number of individuals potentially affected.

12 DPA’s Joint Statement on Scraping
In a rare step, twelve DPAs including the UK and Norway have issued a Joint Statement on Scraping. It’s focussed on scraping personal data from publicly available information on social media, and it’s more of a letter addressed to the social media companies to urge them to prevent scraping of publicly available personal data, but there are a couple of interesting things it says – and does not say.
The DPAs confirm such personal data is still generally covered by data protection laws – although they can’t say ‘always’ as there are exemptions for publicly available data, for example, in some US state laws.
There’s not much new here, apart from the fact this is a joint statement by a dozen DPAs. Interestingly, no EU DPAs are signatories, and only one from the EEA. It remains to be seen whether we should read anything into that.
- What is interesting is the timing, with the EU Digital Services Act now applying to extremely large tech companies such as Meta and X (formerly Twitter), more on that below.
- And there’s no express mention of AI whereas many large language model AI is famously trained by scraping data. Again, we’re not sure how much to read into this – but hats off to AI & Privacy practitioners such as Oliver Patel and Federico Marengo calling this out.
The EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)
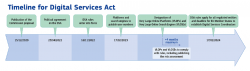
Sticking with assessments, the DSA has started to apply to Very Large Online Platforms and Very Large Online Search Engines and has strict assessment requirements:
Platforms will have to identify, analyse and mitigate a wide array of systemic risks ranging from how illegal content and disinformation can be amplified on their services, to the impact on the freedom of expression and media freedom. Similarly, specific risks around gender-based violence online and the protection of minors online and their mental health must be assessed and mitigated. The risk mitigation plans of designated platforms and search engines will be subject to an independent audit and oversight by the Commission.
A smaller set of obligations will apply to the rest of us in February 2024, so there’s still some time to get to grips with the DSA if it applies to you (territorial scope is very similar to the GDPR).
DSA’s Profiling Opt-out
One of the other aspects that’s attracted lots of attention is user’s ‘right [under DSA itself] to opt-out from recommendation systems based on profiling’.
This opt-out right under the DSA follows closely on the back of the CJEU and DPC decisions on Meta’s use of forced consent or contract as legal bases to carry out behavioural profiling.
Impact on META et al
The Washington Post has a great article on this, linking to a statement by Nick Clegg, Meta’s President, Global Affairs, and ex-UK Deputy Prime Minister which shows that the DSA has forced change both within the organisation:
‘We assembled one of the largest cross-functional teams in our history, with over 1,000 people currently working on the DSA, to develop solutions to the DSA’s requirements. These include measures to increase transparency about how our systems work, and to give people more options to tailor their experiences on Facebook and Instagram. We have also established a new, independent compliance function to help us meet our regulatory obligations on an ongoing basis.’
And in how their users are protected when using the service:
‘We’re now giving our European community the option to view and discover content on Reels, Stories, Search and other parts of Facebook and Instagram that is not ranked by Meta using these systems. For example, on Facebook and Instagram, users will have the option to view Stories and Reels only from people they follow, ranked in chronological order, newest to oldest. They will also be able to view Search results based only on the words they enter, rather than personalised specifically to them based on their previous activity and personal interests.’
The Future of Privacy Forum has a great briefing on the DSA, looking at interplay with the GDPR.
AI Regulatory Tension in the UK
Back in Q2 we summarised the UK’s White Paper on AI and it’s hinterland. UK Gov decided that no new regulator was needed, and no new regulation would be rushed through – contrary to the EU’s approach with the AI Act (now in the trilogue stage).
We’ve now received the Interim Report on AI Governance from the House of Commons Science, Innovation and Technology Committee.
- The Committee’s Interim Report takes a very practical view of AI and sets out twelve challenges to AI governance and regulation that it recommends the Government addresses through domestic policy and international engagement.
- We won’t repeat the 12 challenges in full but they include Bias, Privacy and IP. The paper is short and well worth reading. In practical terms, the challenges can inform your burgeoning AI risk assessments.
The tension comes from the Committee’s strong recommendation that UK Gov pushes forward with even very limited regulations on AI, when the government’s White Paper had clearly suggested they weren’t minded to. The Committee’s view on the EU’s AI Act couldn’t be clearer:
We see a danger that if the UK does not bring in any new statutory regulation for three years it risks the Government’s good intentions being left behind by other legislation—like the EU AI Act—that could become the de facto standard and be hard to displace.
Major UK Law Enforcement Breaches
You’ll have read plenty about the recent, large and impactful personal data breaches at police forces in Northern Ireland and London:
- The Police Service of Northern Ireland PSNI accidentally released personal data about officers by accident in responding to an FOI request, showing how hard it can be to put in place cultural changes and consistency in these situations.
- PSNI then had another breach, when devices with personal data was stolen – arrests have been made.
- And in London, similar information about officers in the Met Police was made public after a breach at a supplier.
Key learnings
- Seemingly mundane acts or omissions can lead to horrific risk to individuals, so these breaches are sad reminders to review your risk assessments.
- Humans are inconsistent, so we should all look at processes that can negate or automate solutions to these risks.
- When you do your next risk assessment, do table-top exercises to explore areas you’ve maybe not focussed on before as they seemed too low-tech, too unexciting, or something you’ve done for years and ‘never had a problem with’.
Transfers, NOYB & Fitbit
After bringing down Privacy Shield, ramping up to attack the EU-US DPF, and filing 101 complaints on transfers concerning Google and Facebook, Max Schrems’s not-fot-profit has now filed complaints with the Austrian, Dutch and Italian DPAs concerning Fitbit, owned by Google.
- The complaints focus on Fitbit’s reliance on consent for transfers of personal data outside the EEA. And this is special categories of personal data as it’s almost entirely about health.
- noyb raise concerns with the validity of the consent, not least for lack of transparency, and the practicalities of withdrawing consent.
This will be one to watch, not least about noyb’s complaint that Fitbit’s Privacy Policy doesn’t set out the specifics of transfers of personal data, for example naming each destination country.
AirBnB, ID Verification & The DPC
Ireland’s DPC has issued a reprimand – not a fine – against AirBnB. The case focussed on AirBnB’s processes to verify the identity of hosts on the platform and contains some good takeaways.
Legitimate Interests
In summary AirBnB did have a legitimate interest in protecting users of the platform, particularly as they may very well meet in real life when attending the property. And it was necessary to check the official ID of hosts for that legitimate interest, notably and particularly as AirBnB had first tried to establish the host’s identity in another way, which had failed.
- Takeaway – This is another decision, alongside the CJEU Meta decision, with examples of acceptable legitimate interests. Whether they then pass the balancing test is another matter.
The DPC was happy that the data subject’s interests did not override AirBnB’s legitimate interests, ie: the rights of the host were not prejudiced.
Data Minimisation
In these particular circumstances, the DPC decided that AirBnB had complied with the principle of data minimisation as photo ID was only asked for after the initial method had failed.
However, AirBnB retained the copy of the ID for the duration of their agreement with the host. The DPC decided this failed both the data minimisation and storage limitation principles as it would have been sufficient to just keep a record that, eg, a passport had been verified on X date.
AirBnB had not convinced the DPC that retention beyond that initial phase was ‘relevant, adequate and limited to what was necessary for the purposes for which the data was collected’.
- Takeaway – Check your retention periods, particularly if you collect ID and see if you can get rid of ID you no longer need – is a record you checked it enough?
Retention
As above, the DPC decided that retaining the copy ID beyond establishing the host’s ID failed the storage limitation principle. The DPC also decided that AirBnB could not retain ID for its other claimed purposes.
For example AirBnB had retained expired and redacted ID as well as accepted ID on the basis it needed it for security improvement purposes including comparative reviews of authentic and fraudulent ID. The DPC disagreed.
Forced consent
The complainant said they’d been forced to consent to the ID processing with no way to withdraw consent. However, the DPC was satisfied that AirBnB relied on legitimate interests, not consent, so this was not relevant.
Transparency
The DPC pointed to the many entries in AirBnB’s Privacy Policy and Terms that referred to ID verification processes, the potential need for official photo ID etc and decided that AirBnB had met their transparency obligations.
- Takeaway – a decent Privacy Policy and Privacy notices at the point of use, plus records of what was shown and when, are invaluable in some complaint situations.
Ciao and Hallo as Languages come to Keepabl!
We’re delighted to announce you can now use Keepabl in German and Italian.
We’ve worked with professional, native-speaking translators familiar with Privacy and B2B SaaS for high-quality translations. French and Spanish are coming soon.
As with all of Keepabl, languages are super simple to use:
- Admins can set the default language for your organisation.
- Individual users can choose to override that default with their own language choice.
Do contact us to see for yourself, book your demo now!
Don’t forget to signup!
Subscribe to our newsletter to get these practical insights into your inbox each month (ok, so we missed July…)
Related Articles

Blog
What is Schrems II?
The Schrems II decision came out nearly 2 years ago, on 16 July 2020. Given the enormous data flows from the EEA and UK to the USA, and many unanswered…

Blog
Biometric data in financial services: existing law, deep fakes, and the UK ICO's draft guidance
This article was first published in Thomson Reuters Regulatory Intelligence on 20 September 2023 and are the personal views of the author, Robert Baugh. Subscribers link. Free trial link. Biometrics have…

